What is Business Continuity Management?

Pre-Event Preparation
Assessment of risks and threat scenarios and how to mitigate or resolve them.
Event Management
In the occurrence of a disaster several activities should be carried out to manage and mitigate the event and its effects.

Post-Event Continuity
Activities that are carried out after the occurence of an event.
What are the diffent actions to take during Pre-Event Preparation? 22, pp.40-44
- Focus is the risk that all physical business locations face
- Important areas to cover during a risk assessment are ‘Building Protection Measures’, ‘Fire Detection and Suppression Measures’ and an assessment of the immediate physical neighborhood
- The Process of Risk Assessment can be displayed as a 6-step cycle
- A major tool for a Site Risk Assesment can be a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Analyzes the impact of disruptions on business functions
- Foundation of Business Continuity Planning
- Four objectives of this phase:
-
1) Determine Crisis Impact to organization
2) Identify Critical Processes, their maximum period of tolerable disruption, recovery time objectives, and recovery point objectives
3) Determine sequence of business function recovery
4) Identify recovery strategies, minimum resources, and vital records - The goal of a Business Impact Analysis is to determine the possible effect a crisis might have
- It has several important activities, the most important are:
-
1) To perform a BIA at every business location
2) Determine potential implications of unavailability of certain business functions or locations
3) Rating of Business processes based on their impact in case of unavailability
4) Obtain detailed understanding of all business processes
5) Define recovery point and time objectives
6) Analyze existing Business Continuity Strategies and identify resource requirements for these
7) Obtain Management approval for the results of the Business Impact Analysis - A business impact analysis is usually conducted by interviewing business managers or key service delivery heads
- BPRA is only performed for critical and important business functions that were identified during the BIA
- Its purpose is to evaluate the risk that the occurrence of a crisis has on resources other than premises as determined in the Site Risk Assessment
- The goal is to identify single points of failure that could lead to a disruption of service
- Creation of a thorough and actionable plan that is reviewd with stakeholders
- is the main source for business continuity information, roles and duties, activities, and procedures that will allow for a quick reaction to a crisis
- This process is owned by the business continuity manager
- Service level arrangements should be made with all major vendors of equipment and services that support the organization
- The goal is to repair/replace services and equipment within the previously defined recovery objectives
- Depending on the role and awareness for BCM and process risks employees need to be trained and made sensitized
- After BCM policies and procedures have been proposed they need to be evaluated and tested through exercises
- All BCM policies and procedures should be reviewed by executive management and auditors
- This process should be documented in the Business Continuity Plan
- Together with this, a Business Continuity Maintenance Plan should also be defined to ensure the continued effectiveness and timely relevance of the topic
What are the different actions to take during Event Mangement? 22, pp.45-46
- These activities are immediate and short term responses to a recently occurred crisis
- The rapid mitigation of immediate damage and notification of all connected stakeholders are the main goals
- A Command Post and Emergency Operations Center should be set up for on site coordination
- After having initiated the immediate emergency response, public authorities should be given notice and control of the situation
- Damage needs to be assessed in two phases
- 1) Evaluation of recovery options and invocation of BC plan
2) Comprehensive evaluation of damage done
- 1) Evaluation of recovery options and invocation of BC plan
- Hardware and Facilities need to be salvaged after a crisis or disaster
- It is important to give insurance companies the ability to assess any damage before salvage takes place
- It is important to document the salvage process
- To allow the resumption of critical business operations, a secondary site should be installed and used
- The secondary site can be a cold, warm or hot side depending on the capabilities and needs of a particular business
- Offical spokespeople should handle any communication at the disaster site
- In order to comply with any insurance policy, the damage assessment team should thoroughly document any damages and recovery efforts and estimate damages
What are the different actions to take during Post-Event Continuity? 22, pp.46-47
- Once the primary site stabilizes past disaster, the business activites at this site should be restored
- The disaster is not yet considered as “over” and to do so, all activities at the primary site must be restored
- To keep the Business Continuity Plan up to date and current it should be reviewed and audited in regular intervals
- A few hours should be assigned in every quarter for this review process by senior management
- Identified changes from the review should be added to the Business Continuity Plan as part of process
- The Triggers of the update can be calendar or event based
- Eventually all generated documentation should be used to submit insurance claims
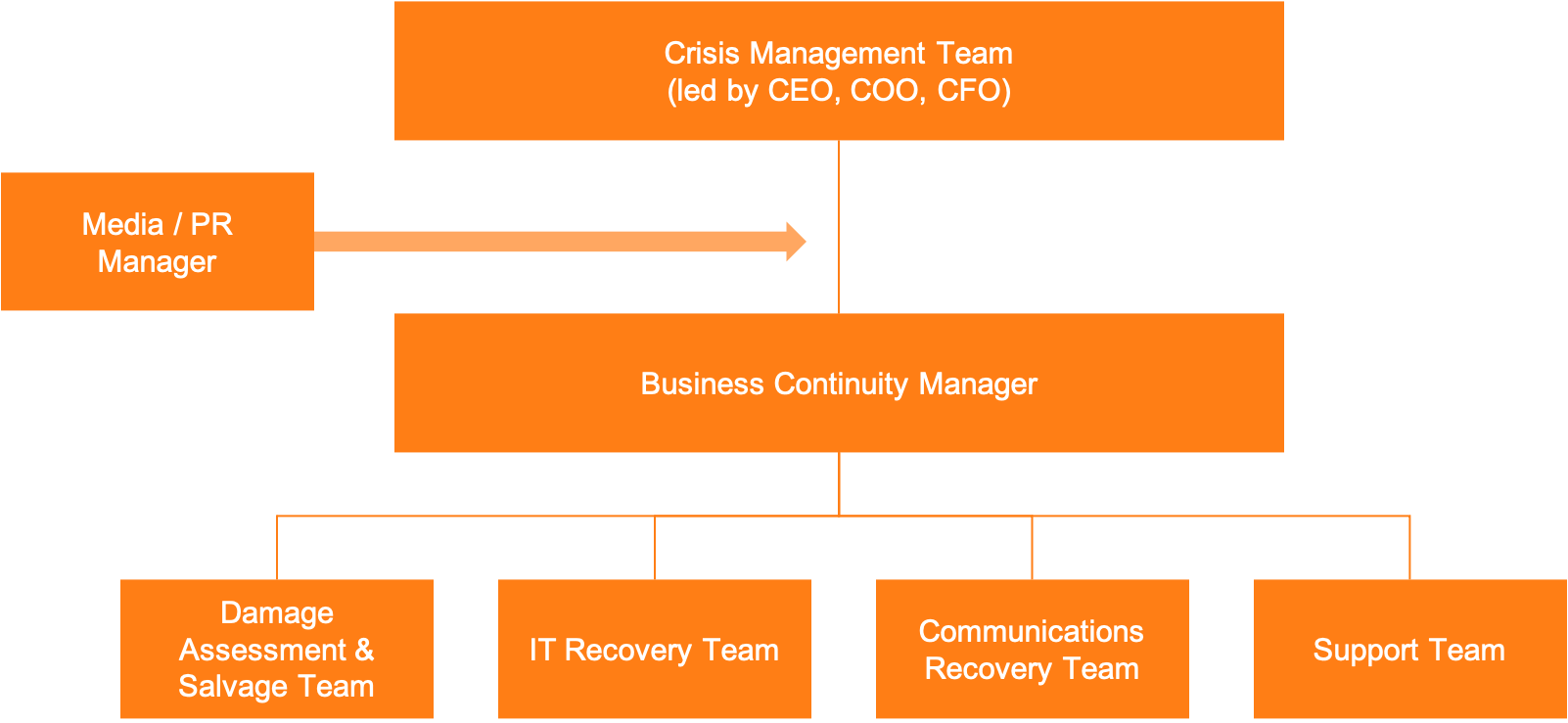
How should an organization be built to effectively practice BCM? 22, pp.37-40
The BCM team should be made up of people from within the organization who also understand this organization 22, p.38, ideally with people who hold the same or similar responsibilities outside of crisis situations also. 22, p.40
BC Manager
- Oversee the development and testing of BCM plans
- These plans should include
- - Training of team members
- Contact lists of key employees
- Vendor agreements
- - Training of team members
- The BC manager should be suitably qualified and should also have a designated backup
- Ideally Person with Media/Journalistic Experience as spokesperson
- Everyone else is to be instructed not to comment on in case of disaster/crisis
- Responsibilities: announcement to other employees and the public
- First responders to any disaster/crisis by determining original state of situation
- Declaration of inventory of damaged and undamaged assets in case of crisis
- Mitigating damage
- Filing of repair and preplacement orders/actions
- Assistance in any legal claims
- Restoring network and IT activities in case of damage by crisis or disaster
- Responsible for all technical or logistical tasks in connection with IT recovery
- Responsible for restoring IT service to the pre-crisis state as well as supporting the “incremental continuity requirements of critical business processes”
- Works closely with IT Recovery Team and is responsible to reestablish communication services in case of disaster/crisis in this field
- Responsible for support actions such as building management, facility support, finance, funding, procurement, HR, personnel tracking, travel, accommodation or communication forwarding in case of disaster or crisis
Additional explanations/zusätzliche Erläuterungen
| Nr. | Phase(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Post Event Continuity | |
| 2 | Event Management | |
| 3 | Risk analysis and evaluation | |
| 4 | Development of the BC Plan | |
| 5 | Business Impact Analyse |


